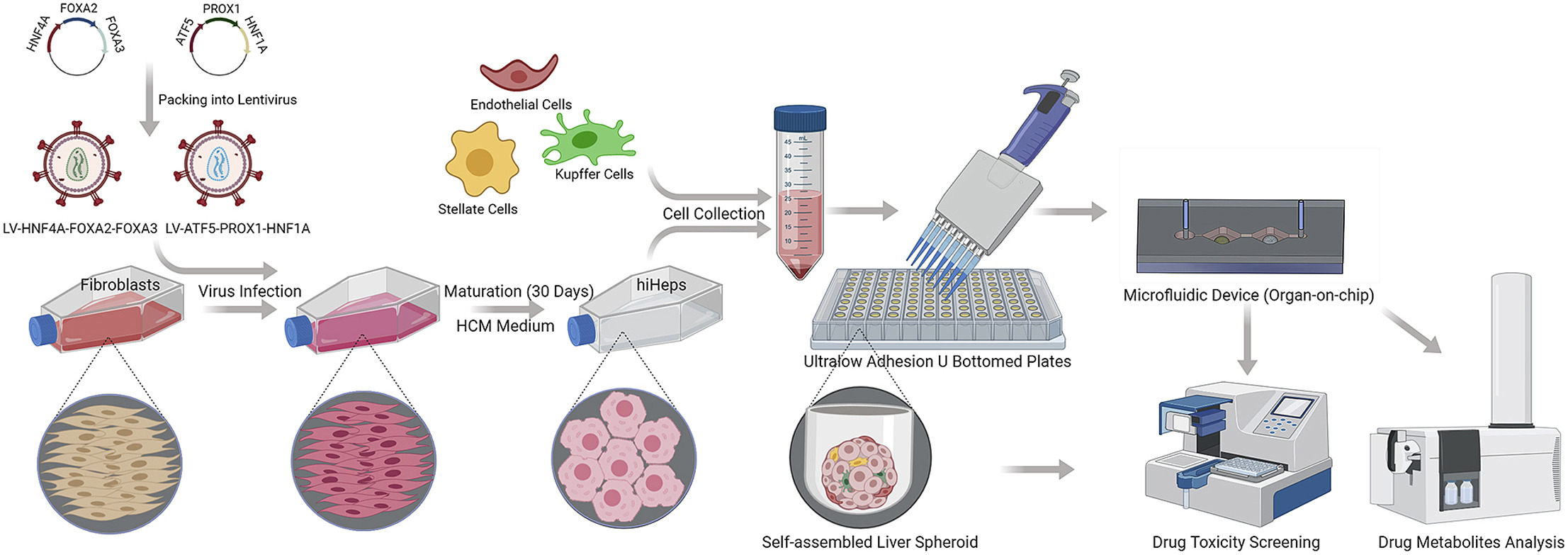
一种通过重编程构建的无框架微肝组织,用于药物代谢测试。
Introduction
产生微肝组织可以概括肝功能,对于组织工程和药物筛选愈发重要。然而原代肝细胞的难以获取以及长时间培养中的肝功能丢失限制了其在药物筛选中的大规模应用。肝肿瘤细胞系,如HepG2肝细胞瘤细胞,由于缺乏原代肝细胞的多种功能且基因不稳定,不能忠实地预测药物毒性和有效性。
为了克服这个限制,研究者尝试从人胚胎干细胞分化肝细胞和诱导多能干细胞。然而,这些肝细胞不适用于个性化药物筛选或者难以获得。
最近,已经可以通过强制表达转录因子,重编程成纤维细胞为肝细胞样细胞。这个过程通常需要多个载体分别表达多种转录因子。由于细胞不能接受所有重编程因子,重编程效率不能让人满意。在一个载体上表达多个转录因子是一个有效改善重编程效率的方法。
三维无框架微肝球是功能化的三维肝模型,可以在长时间培养中维持肝细胞表型。此前研究表明,无框架微球可以提供具有特定三维细胞巢的肝细胞,模拟体内复杂性和结构,在组织工程和药物开发中具有巨大潜能。
本研究作者探索了一种改进方法以传递重编程因子用于人诱导肝细胞的重编程,使人诱导肝细胞和非实质细胞在微流控平台上形成微肝球。展示了人诱导肝细胞兼容于肝微球和他们的微流控平台,具有个性化药物评估的潜力。
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the induction of hiHeps via direct reprogramming
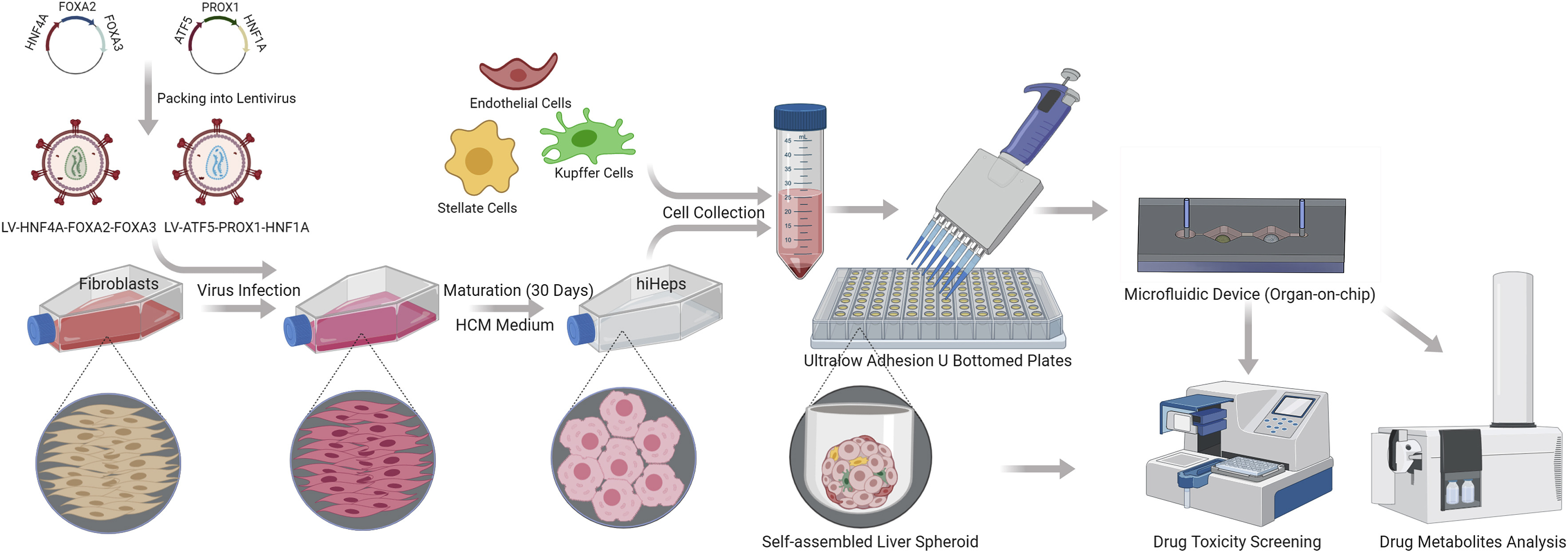
人成纤维细胞被表达6种人肝转录因子的慢病毒转染,诱导直到30天以重编程。随后由人诱导肝细胞(hiHeps)和非实质细胞形成的人诱导肝细胞来源的肝微球通过重力聚集在超低粘附U型孔板。最后,人诱导肝细胞来源的肝微球和肿瘤类器官被放在2器官微流控系统用于药物有效性评估。
Fig. 2. Generation and characterization of human induced hepatocyte-like cells (hiHeps) from human fetal fibroblasts (HFFs) and human adult fibroblast (HAFs)
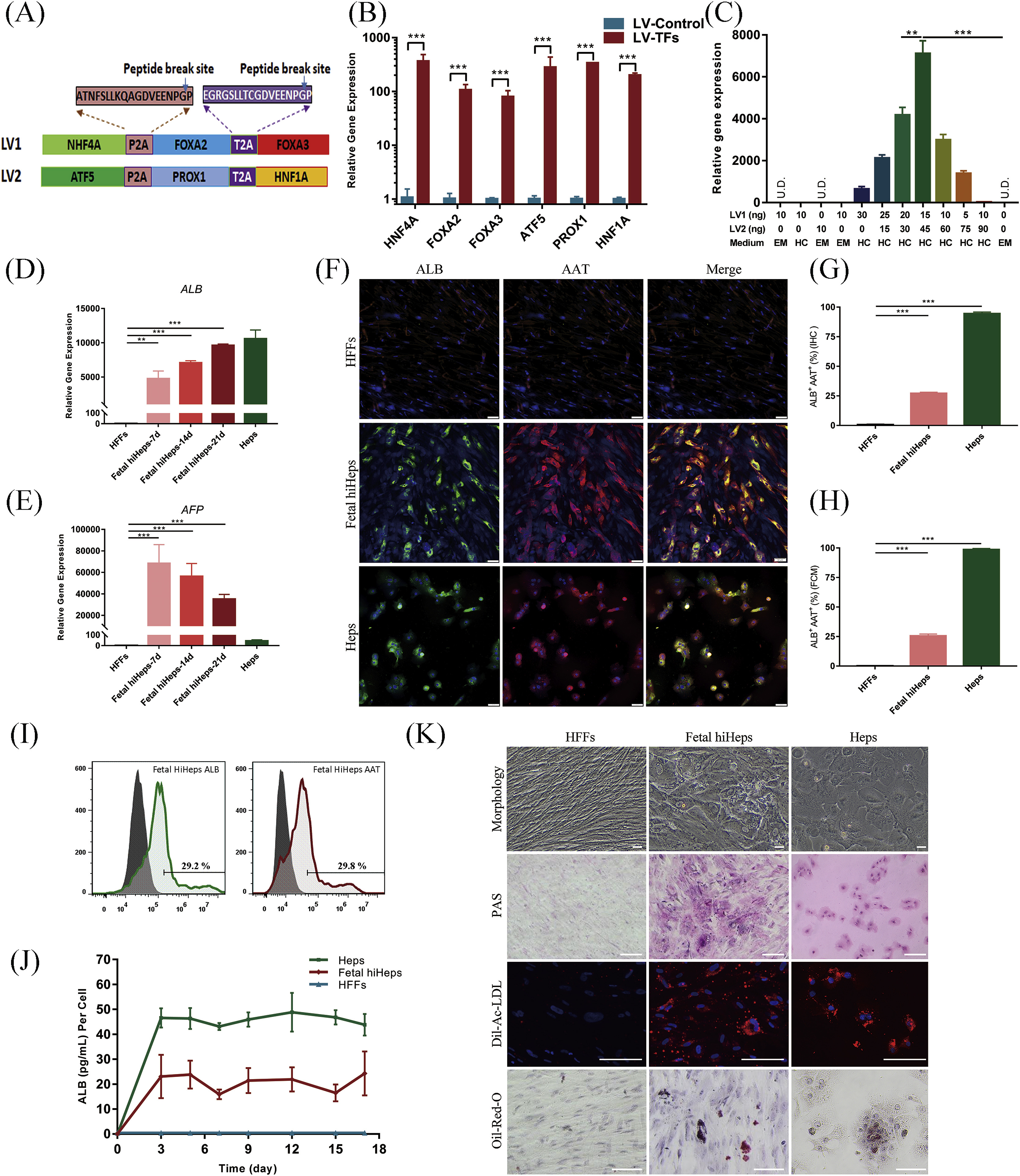
- (A)每个慢病毒载体上表达的肝转录因子。图上列出了序列和预测的P2A/T2A断裂位点。
- (B)RT-qPCR检测转导2天后6种转录因子的表达。GFP表达的慢病毒转导的细胞作为阴性对照。
- (C)优化条件以获得最高的重编程效率。在处理IMR-90细胞14天后使用RT-qPCR检测ALB基因表达。
- (D-E)RT-qPCR分析重编程过程中ALB和AFP基因表达。IMR-90细胞被重编程。
- (F-H)免疫荧光染色和定量分析人胚胎诱导肝细胞中的肝蛋白ALB和AAT。
- (I)IMR-90细胞重编程30天后流式细胞术检测ALB和AAT阳性细胞。
- (J)培养基中ALB分泌的ELISA结果。
- (K)重编程30天后,显示出与成纤维细胞不同的形态。它们显示出明显的低密度脂蛋白(ac-LDL)摄取活性、脂滴的积累(基于油红O染色)和糖原合成(PAS染色),是成熟肝细胞的特征。
关于2A肽介绍,点这。
ALB:albumin,白蛋白,成熟肝细胞marker;AFP:alpha fetoprotein,甲胎蛋白,未成熟肝marker;AAT:alpha-1 antitrypsin,α1-抗胰蛋白酶,肝细胞marker。
Fig. 3. Characterization of drug metabolic-associated gene expression and enzyme activities of hiHeps
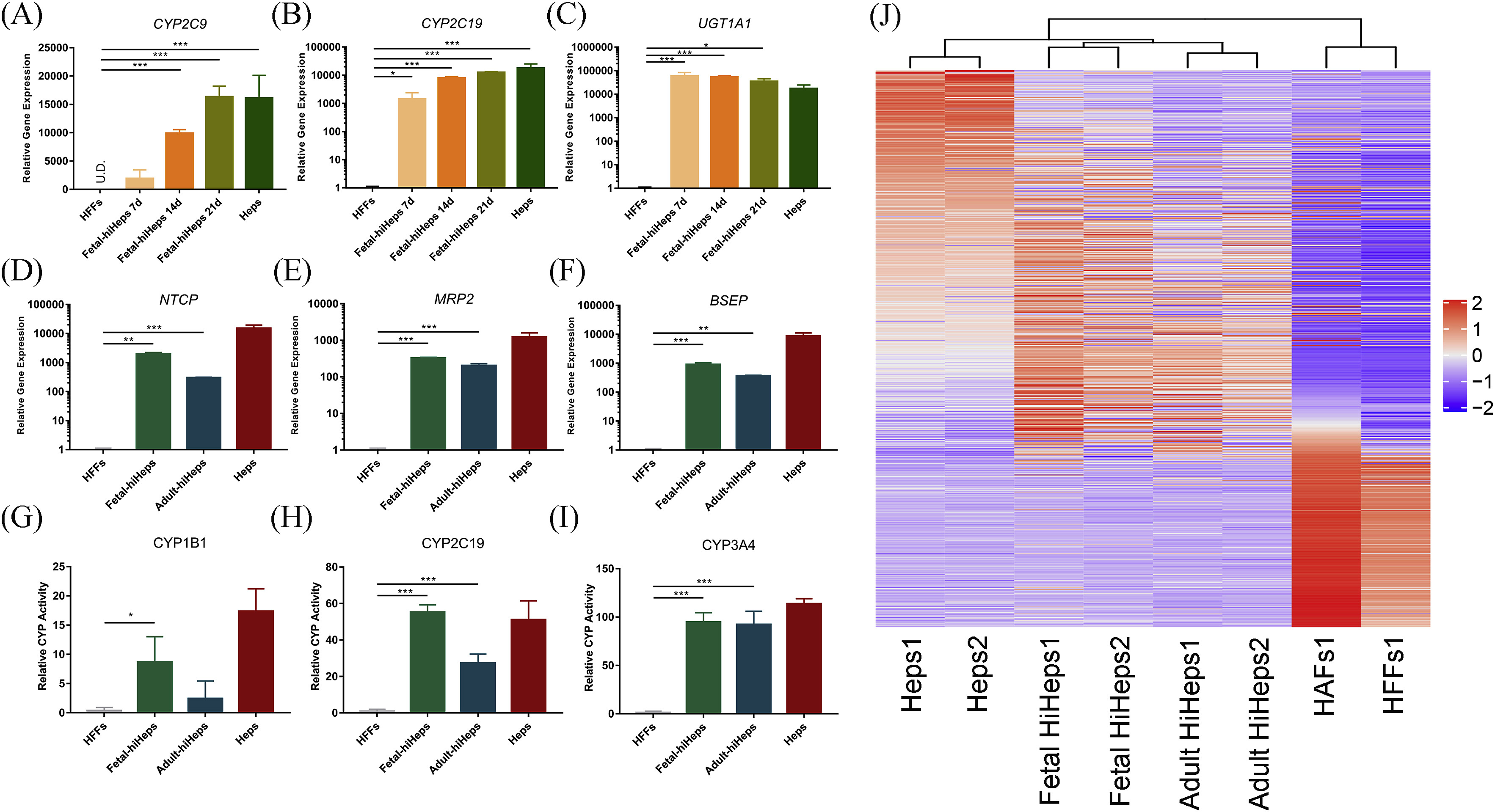
- (A-C)RT-qPCR检测编码肝I相、II相药物代谢酶的基因表达。
- (D-F)RT-qPCR检测编码肝III相药物代谢转运体NTCP、MRP2和BSEP的基因表达。
- (G-I)检测CYP1B1、CYP2C19和CYP3A4的Cyp450代谢活性。
- (J)代谢相关基因表达分析的层次聚类同样揭示了hiHeps与原代肝细胞接近以及在转化过程中纤维化基因被有效沉默。
Fig. 4. Characterization of 3D microlivers
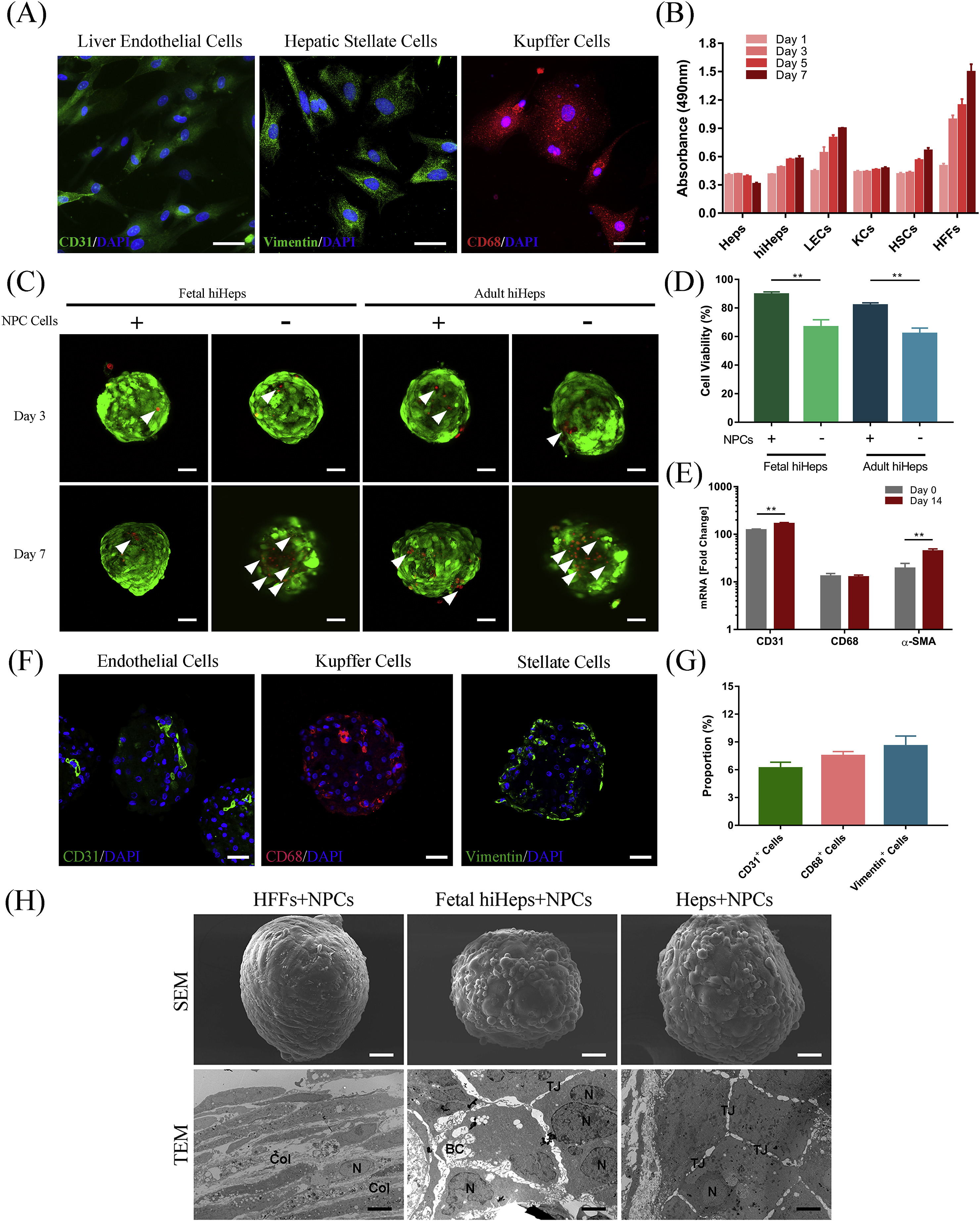
- (A)肝非实质细胞(NPC)细胞标记物的免疫荧光染色检测。CD31、波形蛋白(vimentin)和CD68被分别当作内皮细胞、肝星状细胞和枯否细胞的标记物。
- (B)MTT试验分析NPC细胞在肝细胞培养基中的活性。
- (C)微球的活死染色。
- (D)定量比较7天时微球中的细胞活性。包含NPCs对微球中的细胞生存有改善作用。
- (E)RT-qPCR检测微球中NPC标记物,表明了肝内皮细胞(CD31)、枯否细胞(CD68)和肝星状细胞(α-平滑肌动蛋白/α-SMA)的存在。
- (F-G)免疫荧光染色检测人胚胎hiHeps来源微球中的NPC标记物。
- (H)人hiHeps微球的超微结构。胶原聚集(Col)、细胞核(N)、紧密连接(TJ)和胆小管(BC)标记在图上。
Fig. 5. Characterization of human hiHeps-derived 3D microlivers
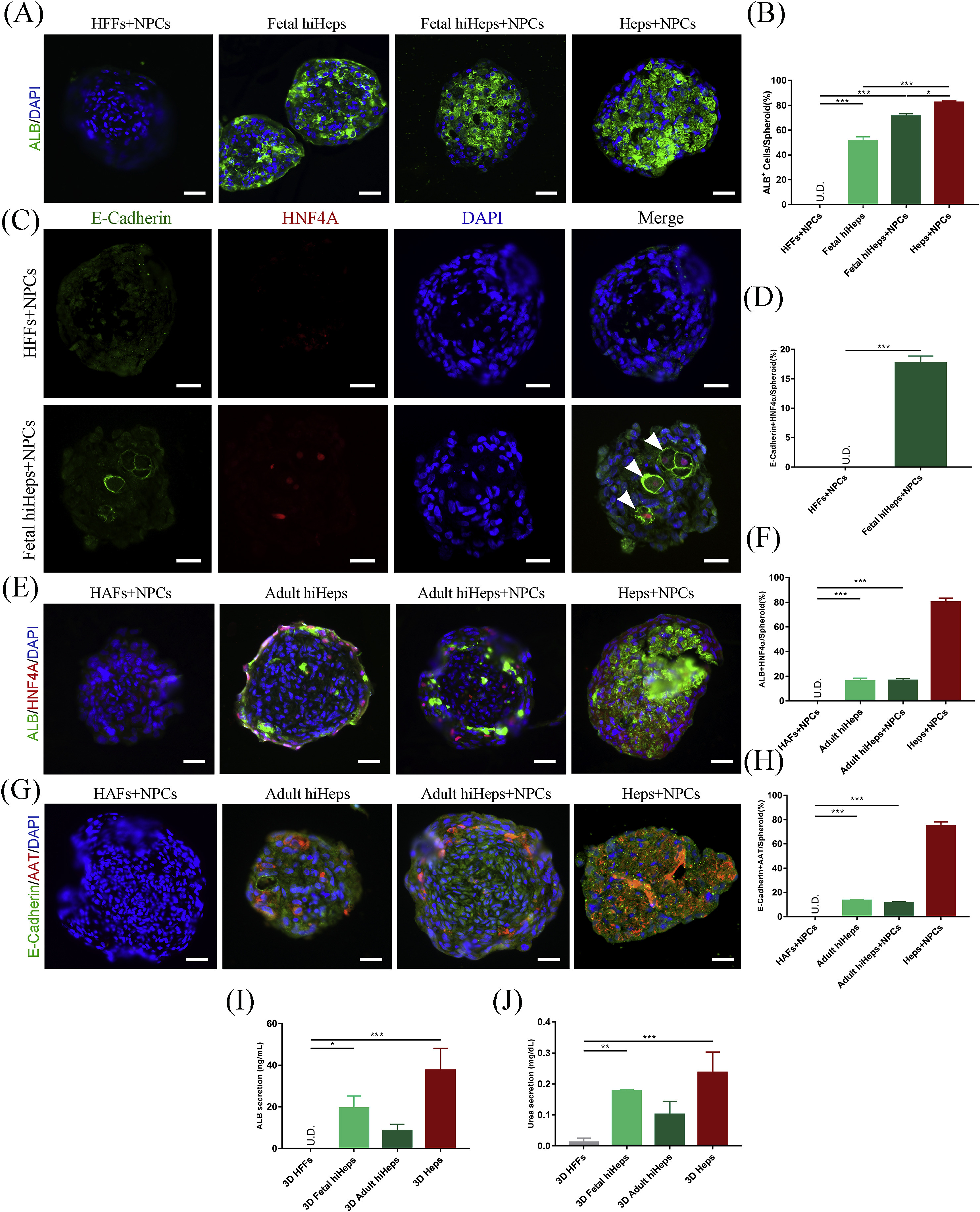
- (A-B)免疫荧光染色检测胚胎hiHeps来源微球中的白蛋白(ALB)。
- (C-D)免疫荧光染色检测胚胎hiHeps来源微球中的上皮标志物(E-cadherin,白色箭头)和肝转录因子HNF4A。
- (E-F)免疫荧光染色检测成人hiHeps来源微球中的ALB和HNF4A。
- (G-H)免疫荧光染色检测成人hiHeps来源微球中的E-cadherin和AAT。
- (I-J)ELISA分析30天时hiHeps来源微球的白蛋白和尿素分泌。
Fig. 6. Characterization of liver spheroids’ hepatocyte-related metabolic genes
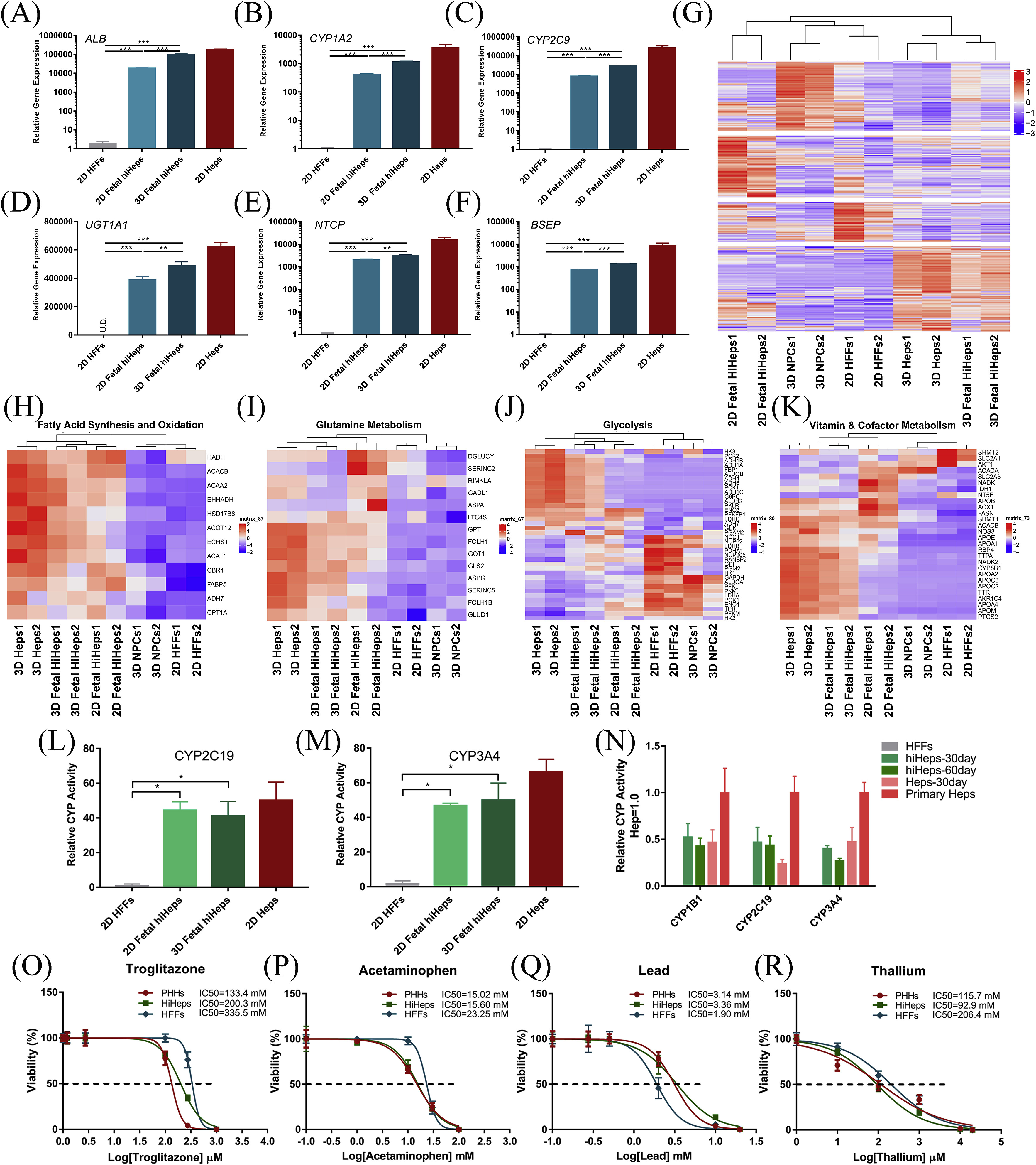
- (A-F)RT-qPCR分析白蛋白和编码药物代谢酶的基因。可以看到3D微球比2D培养具有更高的表达。
- (G)不同代谢通路的基因表达分析。可以看到3D胚胎hiHeps与原代人肝细胞(Heps)比较接近。
- (H-K)脂肪酸合成和氧化(H)、谷氨酰胺代谢(I)、糖酵解(J)以及维生素和辅因子代谢(K)的基因表达分析。
- (L-M)15天时的Cyp450代谢活性。
- (N)30天和60天时的Cyp450代谢活性。
- (O-R)分析4种物质(曲格列酮、对乙酰氨基酚、铅、铊)的慢性毒性。3D培养的hiHeps微肝与Heps微球具有相似的IC50值。
Fig. 7. Validation of capecitabine-metabolizing activity of the hiHeps with a 2-organ chip system
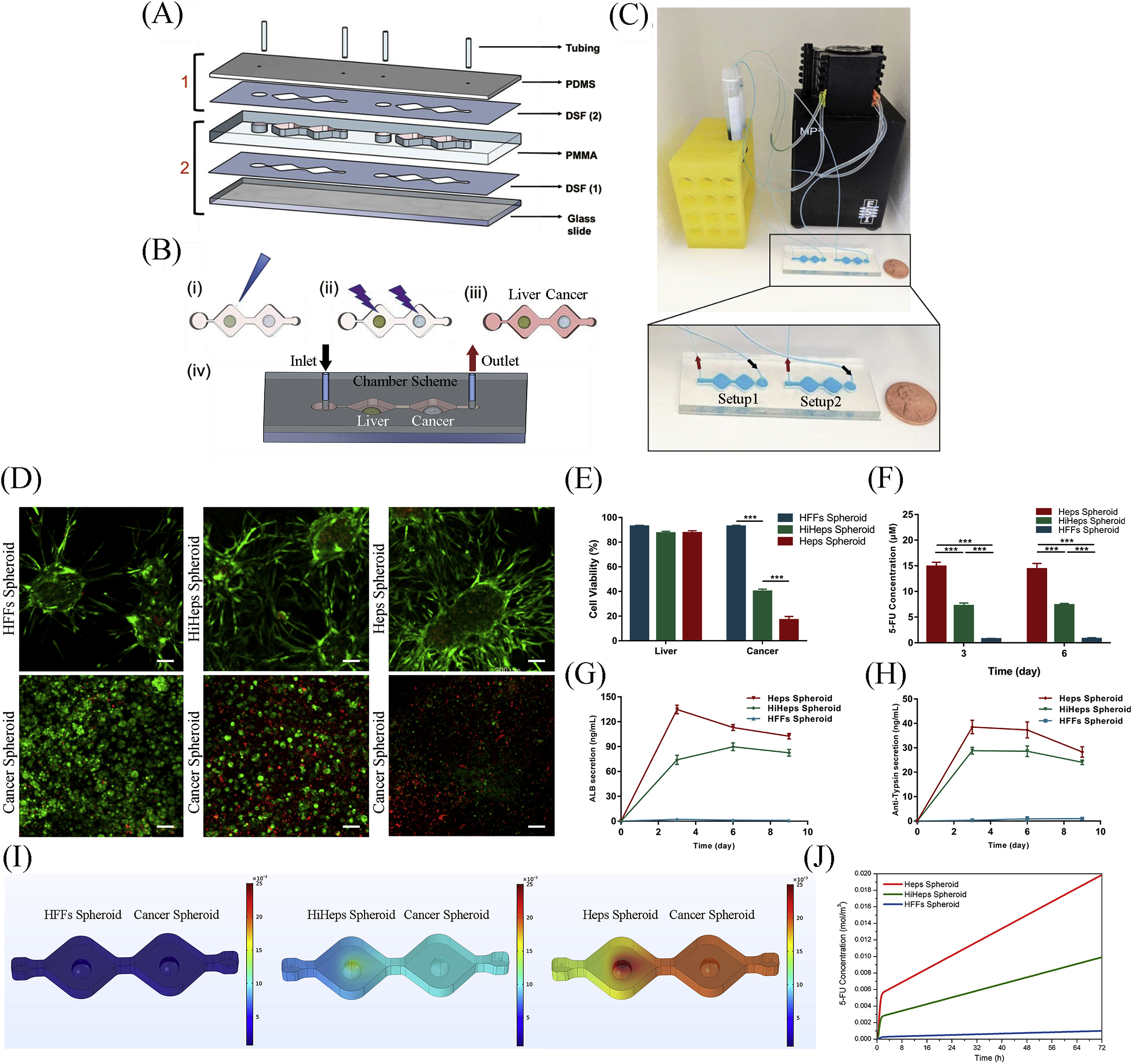
- (A)双器官芯片系统示意图。1为顶部组件,2为底部组件。
- (B)原位制造微球的步骤:
- 将悬有微球/细胞的水凝胶移液到小腔内。
- 将光交联水凝胶暴露在紫外线下1秒。
- 添加培养基到每个小腔。
- 密封顶部组件并连接端口。
- (C)双器官芯片的实验步骤。芯片通过蠕动泵以闭环方式连接到带有培养基/药物的容器中。抗肿瘤前药卡培他滨通过肝转化成5-FU。
- (D)肝和癌细胞球的活死分析。
- (E)微球中细胞活性的定量。
- (F)培养3天和6天时培养基中5-FU代谢浓度。
- (G)ELISA分析培养基中ALB分泌。
- (H)ELISA分析培养基中AAT分泌。
- (I)模拟第3天时双器官芯片系统中5-FU分布。
- (J)模型预测3天中双器官芯片系统中5-FU释放。
Discussion
- 在一个慢病毒载体上表达多个转录因子对iPSC更高效,将这一策略首次迁移至肝细胞重编程。
- 作者发现重编程的肝细胞可以以细胞球形式生存并维持功能达30天。此外,NPCs在3D肝细胞球中具有重要作用。
Reference
Lu Z, Priya Rajan S A, Song Q, et al. 3D scaffold-free microlivers with drug metabolic function generated by lineage-reprogrammed hepatocytes from human fibroblasts[J]. Biomaterials, 2021, 269: 120668.